Position tracking based on pure linear acceleration measurements is a difficult problem. To result in actual position values, linear acceleration (i.e. data from an accelerometer minus gravity) needs to be integrated twice. If there is only a minimal bias on the data of one of the tracked axes, the resulting position values will rapidly drift off.
Although it is well possible to increase the performance of such positioning information by sensor fusion with external reference signals (optical system, barometric pressure etc.), in many cases direct forward calculation of position from linear acceleration is required.
Lately we have been working on gradually improving our linear acceleration measurements in accuracy and tried to tune these measurements with various filters in order to gain relatively reliable displacement information.
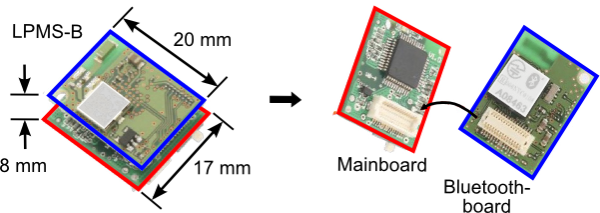
The video below shows an exmaple of displacement tracking on the vertical axis using an LPMS-B device. Except for the sensor’s gyroscope, accelerometer and magnetometer, no external references have been used.